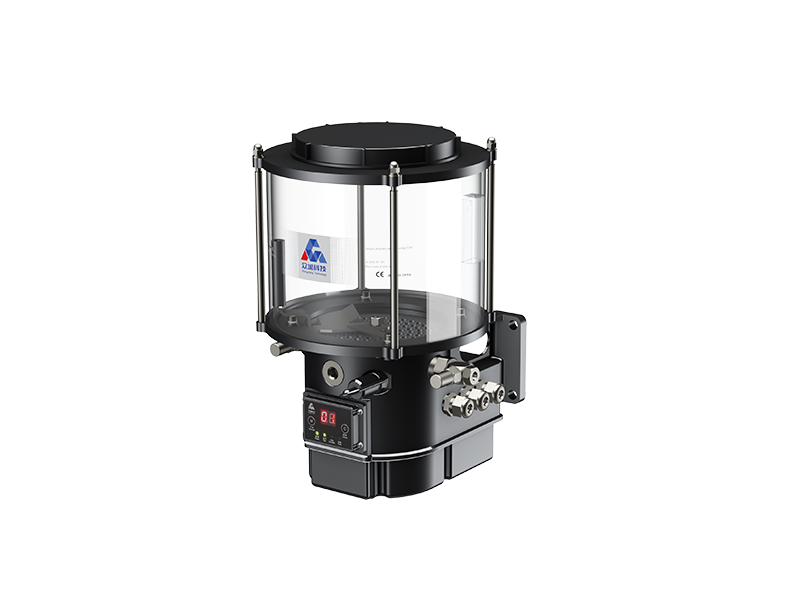
Understanding Metal Wear Particle Sensors: Enhancing Generator Reliability and Performance
Metal wear particle sensors play an essential role in the maintenance and performance optimization of generators and generator sets. These sensors are designed to detect and monitor metal particles that are shed during the wear of mechanical components within the generator. By providing real-time data on particle count and size, these sensors enable operators to gain insights into the wear conditi
Metal wear particle sensors play an essential role in the maintenance and performance optimization of generators and generator sets. These sensors are designed to detect and monitor metal particles that are shed during the wear of mechanical components within the generator. By providing real-time data on particle count and size, these sensors enable operators to gain insights into the wear conditions of critical components such as bearings, gears, and other moving parts.
One of the primary advantages of using metal wear particle sensors is their ability to facilitate predictive maintenance. Traditional maintenance practices often rely on scheduled inspections or reactive measures, which can lead to unplanned downtime and expensive repairs. In contrast, metal wear particle sensors allow for continuous monitoring, enabling operators to identify wear patterns before they lead to significant failures. By detecting the presence of metal particles, operators can make informed decisions about maintenance schedules, ultimately enhancing the reliability and lifespan of their equipment.
Furthermore, these sensors are beneficial for minimizing operational risks in generator systems. Wear debris can lead to catastrophic failures if left unmonitored. For instance, excessive metal particles can indicate problems such as lubrication failure or misalignment, which, if not addressed promptly, could result in severe damage to the generator. By incorporating metal wear particle sensors into their monitoring systems, operators can take proactive measures to mitigate these risks, ensuring safer and more efficient operations.
In addition to improving reliability, metal wear particle sensors contribute to cost savings. By extending the life of generator components through early detection of wear, businesses can reduce maintenance costs and avoid the high expenses associated with unexpected failures. Moreover, these sensors can help optimize the maintenance supply chain by allowing operators to inventory and manage spare parts more effectively, as they can predict when components are likely to require replacement.
As technology advances, the integration of metal wear particle sensors with digital monitoring systems is becoming increasingly common. Many modern generators have the capability to transmit sensor data to centralized monitoring systems, allowing for comprehensive analysis and remote monitoring. This integration provides operators with detailed insights into wear trends and can significantly enhance decision-making processes.
In conclusion, metal wear particle sensors are invaluable tools for professionals in the electrical and power generation sectors. By providing real-time insights into wear conditions, they promote predictive maintenance, enhance equipment reliability, reduce operational risks, and contribute to cost efficiency. For organizations looking to optimize their generator performance, investing in metal wear particle sensors is a strategic move that can lead to substantial long-term benefits.
One of the primary advantages of using metal wear particle sensors is their ability to facilitate predictive maintenance. Traditional maintenance practices often rely on scheduled inspections or reactive measures, which can lead to unplanned downtime and expensive repairs. In contrast, metal wear particle sensors allow for continuous monitoring, enabling operators to identify wear patterns before they lead to significant failures. By detecting the presence of metal particles, operators can make informed decisions about maintenance schedules, ultimately enhancing the reliability and lifespan of their equipment.
Furthermore, these sensors are beneficial for minimizing operational risks in generator systems. Wear debris can lead to catastrophic failures if left unmonitored. For instance, excessive metal particles can indicate problems such as lubrication failure or misalignment, which, if not addressed promptly, could result in severe damage to the generator. By incorporating metal wear particle sensors into their monitoring systems, operators can take proactive measures to mitigate these risks, ensuring safer and more efficient operations.
In addition to improving reliability, metal wear particle sensors contribute to cost savings. By extending the life of generator components through early detection of wear, businesses can reduce maintenance costs and avoid the high expenses associated with unexpected failures. Moreover, these sensors can help optimize the maintenance supply chain by allowing operators to inventory and manage spare parts more effectively, as they can predict when components are likely to require replacement.
As technology advances, the integration of metal wear particle sensors with digital monitoring systems is becoming increasingly common. Many modern generators have the capability to transmit sensor data to centralized monitoring systems, allowing for comprehensive analysis and remote monitoring. This integration provides operators with detailed insights into wear trends and can significantly enhance decision-making processes.
In conclusion, metal wear particle sensors are invaluable tools for professionals in the electrical and power generation sectors. By providing real-time insights into wear conditions, they promote predictive maintenance, enhance equipment reliability, reduce operational risks, and contribute to cost efficiency. For organizations looking to optimize their generator performance, investing in metal wear particle sensors is a strategic move that can lead to substantial long-term benefits.